Isomerism of Alcohol
Alcohols exhibits following three types of isomerism. They are Chain isomerism.Position isomerism. Functional isomerism.In the common system of nomenclature,alcohols are named as. $$Alkyl\,+alcohol=Alkyl\,alcohol$$ Structural formula of tertiary butanol is given below and its IUPAC name is 2.methyl propane-2ol
Summary
Alcohols exhibits following three types of isomerism. They are Chain isomerism.Position isomerism. Functional isomerism.In the common system of nomenclature,alcohols are named as. $$Alkyl\,+alcohol=Alkyl\,alcohol$$ Structural formula of tertiary butanol is given below and its IUPAC name is 2.methyl propane-2ol
Things to Remember
- Alcohols exhibits following three types of isomerism.
- Alcohols containing at least 4-carbon atoms form chain isomerism due to the different structure of C-skeleton in the longest chain.
-
In the common system of nomenclature,alcohols are named as.
-
$$Alkyl\,+alcohol=Alkyl\,alcohol$$
-
MCQs
No MCQs found.
Subjective Questions
No subjective questions found.
Videos
No videos found.

Isomerism of Alcohol
Isomerism of alcohols.
Alcohols exhibits following three types of isomerism.
- Chain isomerism.
- Position isomerism.
- Functional isomerism.
Chain isomerism.
Alcohols containing at least 4-carbon atoms form chain isomerism due to the different structure of C-skeleton in the longest chain.
.png)
Position isomerism.
Alcohols containing at least 3 C atoms form position isomerism due to a different position of a hydroxy group (OH).
Example.
.png)
Functional isomer.
Alcohols containing at least 2 carbon atoms give functional isomers. The functional isomer of an alcohol is ether.
Example.
.png)
Nomenclature.
1. Common system.
In common system of nomenclature,alcohols are named as.
$$Alkyl\,+alcohol=Alkyl\,alcohol$$
Example.
$$alkane\xrightarrow{-ane\,+yl}alkyl\xrightarrow{alcohol}Alkyl\,alcohol$$
$$\underbrace{CH_4}_{Methane}\xrightarrow{-H}\underbrace{CH_3}_{Methyl}-\xrightarrow{+OH}\underbrace{CH_3OH}_{Methyl\,alcohol}$$

2. IUPAC systems.
In this system, alcohols are given their respective names by adding suffix-'ol' with word root.
$$Alkane\xrightarrow{+ol}Alkanol$$
Example.
$$CH_4\xrightarrow{+Ol\,-H}\underbrace{CH_3OH}_{Methanol}$$.v

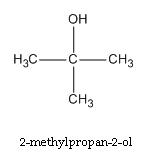
Write down the structural formula and IUPAC name of tert.Butyl alcohol.
Structural formula of tertiary butanol is given below and its IUPAC name is 2.methyl propane-2ol
Some more example of Alcohol

Reference.
Bahl, B S, Bahl, and Arun. Advanced Organic chemistry. S. Chand and company Ltd., n.d.
Sthapit, M K, R R Pradhananga, and K B Bajracharya. Foundations of chemistry. Taleju Prakashan, n.d.
Tewari, K S, S N Mehrotra, and N K Vishnoi. A textbook of organic chemistry. Vikash publishing House Pvt. ltd., n.d.
Verma, N K and S K Khanna. Compressive chemistry. 8th edition. Laxmi publications P. Ltd., 1999.
Lesson
Alcohols and Phenols
Subject
Chemistry
Grade
Grade 12
Recent Notes
No recent notes.
Related Notes
No related notes.