General method of preparation of Alcohol
Haloalkane reacts with aueous alkali or moist AgO to give corresponding alcohols. $$\underbrace{R-H}_{halo\,Alkane}\xrightarrow{aq.alkali\,or\,moist\,Ag_2O}\underbrace{R-OH}_{Alcohol}$$ Aldehydes and ketones from addition product with Grignard reagent. These addition products of hydrolysis in presence of an acid give alcohols. All three types of alcohol )10, 20, and 30) can be prepared by this method.Primary amines react with nitrous acid to give corresponding alcohol. $$\underbrace{R-NH_2}_{Primary\,amine}+HO-NO→\underbrace{R-OH}_{Alcohol}+N_2+H_2O$$
Summary
Haloalkane reacts with aueous alkali or moist AgO to give corresponding alcohols. $$\underbrace{R-H}_{halo\,Alkane}\xrightarrow{aq.alkali\,or\,moist\,Ag_2O}\underbrace{R-OH}_{Alcohol}$$ Aldehydes and ketones from addition product with Grignard reagent. These addition products of hydrolysis in presence of an acid give alcohols. All three types of alcohol )10, 20, and 30) can be prepared by this method.Primary amines react with nitrous acid to give corresponding alcohol. $$\underbrace{R-NH_2}_{Primary\,amine}+HO-NO→\underbrace{R-OH}_{Alcohol}+N_2+H_2O$$
Things to Remember
-
Haloalkane reacts with aqueous alkali or moist AgO to give corresponding alcohols.
$$\underbrace{R-H}_{halo\,Alkane}\xrightarrow{aq.alkali\,or\,moist\,Ag_2O}\underbrace{R-OH}_{Alcohol}$$
-
Carbonyl compounds C=O like aldehyde and ketones as well as other organic compounds such as carboxylic acid, esters, anhydrides are reduced to alcohols by the action of LiAlH4, NaBH4, or H2/Ni
-
$$\underbrace{C=O}_{Carbonyl\,Compound}+2[H]\xrightarrow{reducing\,agent}\underbrace{CH-OH}_{Alcohol}$$
MCQs
No MCQs found.
Subjective Questions
No subjective questions found.
Videos
No videos found.

General method of preparation of Alcohol
General-method-of-preparation-of-alcohol
1. From haloalkane.
Haloalkane reacts with aueous alkali or moist AgO to give corresponding alcohols.
$$\underbrace{R-H}_{halo\,Alkane}\xrightarrow{aq.alkali\,or\,moist\,Ag_2O}\underbrace{R-OH}_{Alcohol}$$
Example.
$$\underbrace{CH_3CH_2Cl}_{Chloro\,ethane}\xrightarrow{aq.KOH}\underbrace{CH_3CH_2OH}_{Ethanol}+KCl$$
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH-BR-CH_3}_{2-bromo\,propane}+Ag_2O(Moist)→\underbrace{CH_3-CH-OH-CH_3}_{2-propanol}+2AgBr$$
2. From carbonyl compounds.
Carbonyl compounds C=O like aldehyde and ketones as well as other organic compounds such as carboxylic acid, esters, anhydrides are reduced to alcohols by the action of LiAlH4, NaBH4, or H2/Ni
$$\underbrace{C=O}_{Carbonyl\,Compound}+2[H]\xrightarrow{reducing\,agent}\underbrace{CH-OH}_{Alcohol}$$
Example.
$$\underbrace{CH_3-COH}_{Ethanal\,or\,Acetaldehyde)}+2[H]\xrightarrow{LiAlH_4}\underbrace{CH_3CH_2OH}_{Ethanol}$$
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CO-CH_3}_{Propanone\,or\,Acetone}+2[H]\xrightarrow{H_2\,Ni}\underbrace{CH_3-CH-OH-CH_3}_{2-Propanol}$$
$$\underbrace{CH_3-COOH}_{Ethanoic\,acid\,or\,Acetic\,acid}+H_2\xrightarrow{Ni}\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-OH}_{Ethanol}+H_2O$$
$$\underbrace{CH_3-COOC_2H_5}_{Ethyl\,ethanoate\,or\,Ethyl\,acetate}\xrightarrow{LiAlH_4}\underbrace{2CH_3-CH_2OH}_{Ethanol}$$
3. From Grignards reagent.
.png)
Aldehydes and ketones from addition product with Grignard reagent. These addition products of hydrolysis in presence of an acid give alcohols. All three types of alcohol )10, 20, and 30) can be prepared by this method.
Preparation of primary alcohol.
Formaldehyde produces addition products with Grignard reagent which on hydrolysis from alcohol
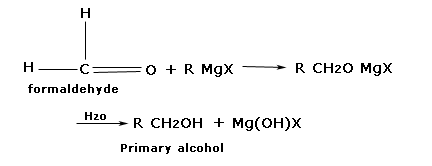
Example

2 preparation of secondary alcohol.
All other aldehydes except formaldehyde produce secondary alcohol when treated with Grignard reagent followed by hydrolysis.

Example.
.png)
3. Preparation of Tertiary alcohol.
.png)
Example.
.png)
4. From primary amines.
Primary amines react with nitrous acid to give corresponding alcohol.
$$\underbrace{R-NH_2}_{Primary\,amine}+HO-NO→\underbrace{R-OH}_{Alcohol}+N_2+H_2O$$
Example.
$$\underbrace{CH_3CH_2NH_2}_{Ethanamine}+HO-NO→\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-OH}_{Ethanol}+N_2+H_2O$$
5. By hydrolysis of ester.
Esters can be hydrolyzed both in acidic and basic medium to give alcohol and carboxylic acid.
$$\underbrace{R-C=O-OR'}_{Ester}+H-OH\xrightarrow{H^+\,or\,OH^-}\underbrace{R-C=O-OH}_{Carboxylic\,acid}+\underbrace{R'-OH}_{Alcohol}$$
Reference.
Bahl, B S, Bahl, and Arun. Advanced Organic chemistry. S. Chand and company Ltd., n.d.
Sthapit, M K, R R Pradhananga, and K B Bajracharya. Foundations of chemistry. Taleju Prakashan, n.d.
Tewari, K S, S N Mehrotra, and N K Vishnoi. A textbook of organic chemistry. Vikash publishing House Pvt. ltd., n.d.
Verma, N K and S K Khanna. Compressive chemistry. 8th edition. Laxmi publications P. Ltd., 1999.
Lesson
Alcohols and Phenols
Subject
Chemistry
Grade
Grade 12
Recent Notes
No recent notes.
Related Notes
No related notes.