Other reaction of Alcohol
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_2=CH_2}_{Ethene}+H_2O$$ $$\underbrace{CH_3-CHOH-CH_3}_{2-Propanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_2=CH-CH_3}_{Propene}$$ $$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-CHOH-CH_3}_{2-butanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_3-CH=CH-CH_3}_{2-butene}+H_2O$$ A primary alcohol is easily oxidised to an aldehyde which gets further oxidised to give a carboxylic acid containing carbon atoms equal to that of alcohols. Tertiary alcohol are not oxidised by neutral or alkaline oxidising agents but acidic oxidising oxidise them. At first, the alkene is formed due to dehydration which is then oxidised to give a mixture of aldehydes, ketones and acids.
Summary
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_2=CH_2}_{Ethene}+H_2O$$ $$\underbrace{CH_3-CHOH-CH_3}_{2-Propanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_2=CH-CH_3}_{Propene}$$ $$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-CHOH-CH_3}_{2-butanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_3-CH=CH-CH_3}_{2-butene}+H_2O$$ A primary alcohol is easily oxidised to an aldehyde which gets further oxidised to give a carboxylic acid containing carbon atoms equal to that of alcohols. Tertiary alcohol are not oxidised by neutral or alkaline oxidising agents but acidic oxidising oxidise them. At first, the alkene is formed due to dehydration which is then oxidised to give a mixture of aldehydes, ketones and acids.
Things to Remember
-
The reaction involving less of a water molecule is known as dehydration . Alcohols are dehydrated in presence of c0nc. H2SO4 or heat alumina to form alkenes.
-
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_2=CH_2}_{Ethene}+H_2O$$
-
A primary alcohol is dehydrogenated easily to produce the corresponding aldehyde.
$$\underbrace{C_2H_5-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{Cu\,300^0C}\underbrace{CH_3-CHO}_{Ethanal}+H_2$$
-
MCQs
No MCQs found.
Subjective Questions
No subjective questions found.
Videos
No videos found.

Other reaction of Alcohol
Other reaction:
1) Dehydration: The reaction involving less of a water molecule is known as dehydration . Alcholos are dehydrated in presence of c0nc. H2SO4 or heataluminania to form alkenes.
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_2=CH_2}_{Ethene}+H_2O$$
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CHOH-CH_3}_{2-Propanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_2=CH-CH_3}_{Propene}$$
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-CHOH-CH_3}_{2-butanol}\xrightarrow{Conc-H_2SO_4\,160^0-170^0C}\underbrace{CH_3-CH=CH-CH_3}_{2-butene}+H_2O$$
Also,
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-CH_2OH}_{1-Propanol}\xrightarrow{Al_2O_3\,350^0}\underbrace{CH_3-CH=CH_2}_{Propene}+H_2O$$
But,
$$\underbrace{C_2H_5-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{H_2SO_4\,100^0C}\underbrace{C_2H_5HSO_4}_{Ethyl\,hydrogen\,sulphate}+H_2O$$
$$\underbrace{C_2H_5-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{H_2SO_4\,140^0C}\underbrace{C_2H_5-O-C_2H_5}_{diethyl\,ether}$$
$$\underbrace{C_2H_5-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{Al_2O_3\,250^0C}\underbrace{C_2H_5-O-C_2H_5}_{diethyl\,ether}+H_2O$$
2) Dehydrogenation: The process of removal of hydrogen from or substrate is called Dehydrogenation. When vapours of alcohol are passed through heated copper at 3000C , they are dehydrogenated to produce different products depending on the type of alcohol taken.
A primary alcohol is dehydrogenated easily to produce the corresponding aldehyde.
$$\underbrace{C_2H_5-OH}_{Ethanol}\xrightarrow{Cu\,300^0C}\underbrace{CH_3-CHO}_{Ethanal}+H_2$$
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-CH-H-OH}\xrightarrow{Cu\,300^0C}\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2CHO}_{Propanol}+H_2$$
Secondary alcohols are also dehydrogenated easily to give corresponding ketones.
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH-OH-CH_3}_{2-Propanol}\xrightarrow{Cu\,,300^0C}\underbrace{CH_3-CO-CH_3}_{Acetone}+H_2$$
$$\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-CH-OH-CH_3}_{2-Butanol}\xrightarrow{Cu\,,300^0C}\underbrace{CH_3-CH_2-CO-CH_3}_{2-butanone}+H_2$$
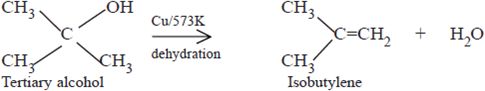
Since tertiary alcohols do not contain or hydrogen, they undergo dehydration instead of dehydrogenation to yield alkenes.
!!!) Oxidation: Alcohols are oxidised by acidified or alkaline KMnO4 , acidified dichromate, and chromic oxide (cross). During oxidation , primary and secondary alcohols from aldehyde and ketones respectively whereas tertiary alcohols are difficult to oxide.
a) Primary alcohol: A primary alcohol is easily oxidised to an aldehyde which gets further oxidised to give a carboxylic acid containing carbon atoms equal to that of alcohols.

b) Secondary alcohol: Secondary alcohol is easily oxidated to the ketone. The ketone is not oxidised under normal condition . However, it forms a mixture of carboxylic acid when oxidised in drastic condition.
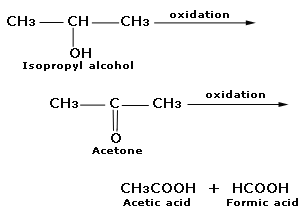
C. Tertiary alcohol: Tertiary alcohol are not oxidised by neutral or alkaline oxidising agents but acidic oxidising oxidise them. At first, the alkene is formed due to dehydration which is then oxidised to give a mixture of aldehydes, ketones and acids.


Reference.
Bahl, B S, Bahl, and Arun. Advanced Organic chemistry. S. Chand and company Ltd., n.d.
Sthapit, M K, R R Pradhananga, and K B Bajracharya. Foundations of chemistry. Taleju Prakashan, n.d.
Tewari, K S, S N Mehrotra, and N K Vishnoi. A textbook of organic chemistry. Vikash publishing House Pvt. ltd., n.d.
Verma, N K and S K Khanna. Compressive chemistry. 8th edition. Laxmi publications P. Ltd., 1999.
Lesson
Alcohols and Phenols
Subject
Chemistry
Grade
Grade 12
Recent Notes
No recent notes.
Related Notes
No related notes.